Always consult a healthcare professional before considering Viagra, especially if you have certain medical conditions. Individuals with a history of heart problems, such as severe heart failure or angina, should avoid this medication, as it can lead to serious cardiovascular events. If you’re currently taking nitrates for chest pain, combining these with Viagra can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
If you suffer from retinitis pigmentosa, a rare genetic eye condition, it’s advisable to steer clear of Viagra. This drug can interact negatively with the underlying issues related to your vision. Additionally, those with a known allergy to any ingredient within Viagra should refrain from use to prevent allergic reactions that could be severe.
Other contraindications include severe liver or kidney problems. In such cases, the body may not metabolize the medication effectively, leading to increased side effects or toxicity. Always share your complete medical history with your doctor to ensure safe usage. Remember, informed decisions contribute to better health outcomes.
- Viagra Medication Contraindications
- Understanding Viagra and Its Uses
- Common Health Conditions That Prohibit Viagra Use
- Drug Interactions and Their Impact on Viagra Efficacy
- Risk Factors for Adverse Reactions with Viagra
- Cardiovascular Conditions
- Drug Interactions
- Underlying Health Issues
- Consultation and Assessment Before Viagra Prescription
- Assessing Risk Factors
- Patient Education
Viagra Medication Contraindications
Do not use Viagra if you take nitrates for chest pain, as the combination can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Avoid using this medication if you are allergic to sildenafil or any of the inactive ingredients in the formulation. Patients with severe liver or kidney issues should consult a healthcare provider before considering Viagra, as adjustments may be necessary.
Individuals with a history of heart problems, such as heart attack or stroke within the last six months, should also refrain from using Viagra unless advised otherwise by a doctor. Additionally, those with low blood pressure or certain eye conditions, such as retinitis pigmentosa, should exercise caution.
Using Viagra in conjunction with other erectile dysfunction treatments, such as alprostadil, can increase the risk of side effects and is not recommended. Discuss any medications, including over-the-counter products and supplements, with your healthcare provider to ensure safety and avoid potentially harmful interactions.
Finally, men with anatomical penile issues, including Peyronie’s disease or conditions that predispose them to priapism (prolonged erection), should not take Viagra without medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication to ensure it aligns with your health status.
Understanding Viagra and Its Uses
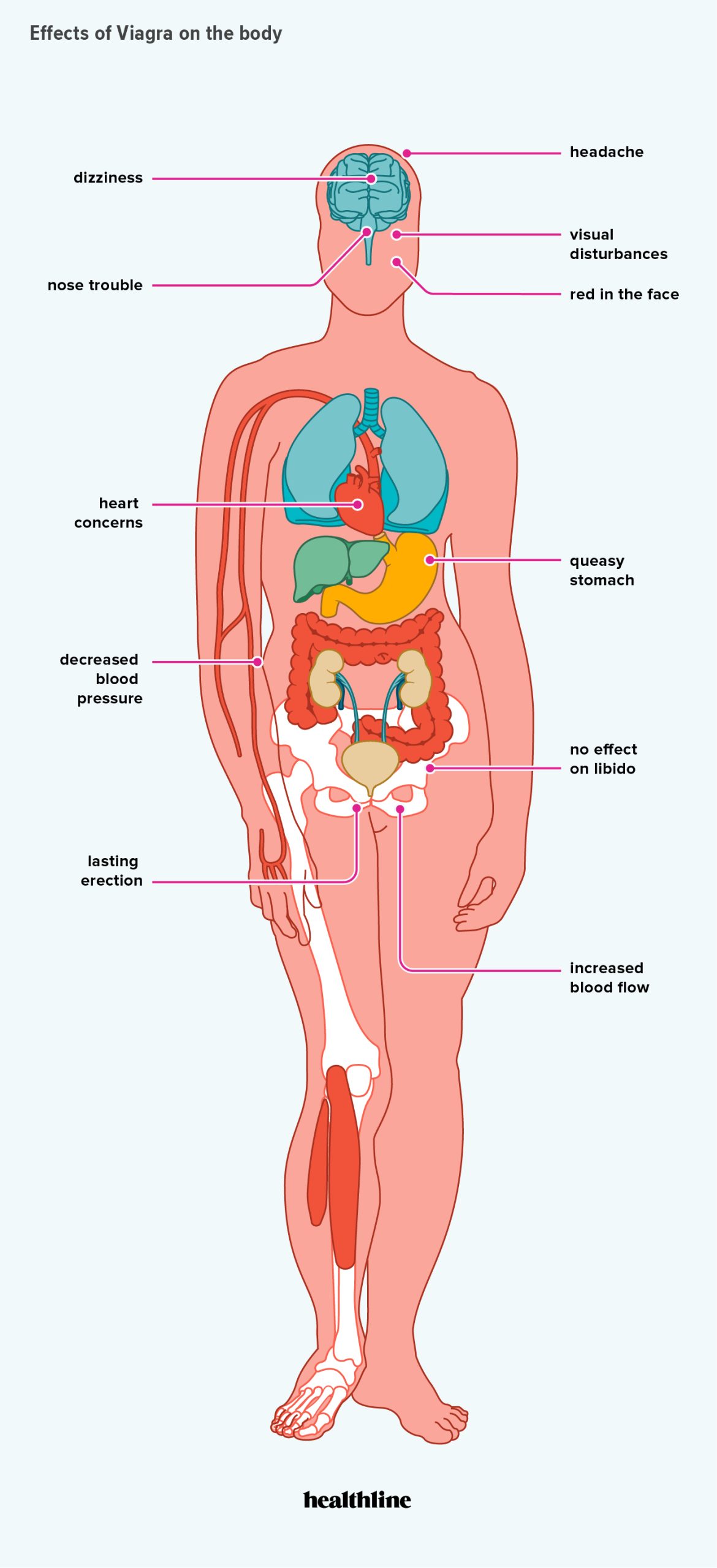
Viagra, known generically as sildenafil, treats erectile dysfunction (ED) by increasing blood flow to the penis. This improvement helps men achieve and maintain an erection during sexual activity.
The medication is effective only when there is sexual stimulation. It does not increase sexual desire but enhances the body’s ability to respond to sexual arousal. Most users find it beneficial about 30 to 60 minutes after intake, lasting up to four hours.
Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Key considerations include:
- Cardiovascular Health: Individuals with severe heart issues, such as unstable angina or recent heart attack, should avoid this medication.
- Blood Pressure: Those taking nitrates for chest pain or nitric oxide donors should not use Viagra, as the combination can lead to dangerously low blood pressure.
- Liver and Kidney Function: Impaired liver or kidney function may necessitate dosage adjustments or complete avoidance of Viagra.
- Eye Conditions: People with a history of vision problems, particularly sudden vision loss, should consult a doctor before use.
Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and indigestion. Serious side effects, though rare, can include priapism (prolonged erection), sudden hearing loss, or severe allergic reactions.
Consult a healthcare professional before starting Viagra to determine if it suits your health profile. Always disclose current medications and health conditions to avoid harmful interactions.
Common Health Conditions That Prohibit Viagra Use
Individuals with specific health conditions should avoid Viagra due to potential risks. Cardiovascular issues, particularly severe heart disease, can lead to complications when taking this medication. Consult with a healthcare provider if you have a history of heart attacks, angina, or uncontrolled hypertension.
Patients using nitrates for chest pain must refrain from Viagra. The combination can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Always disclose any nitrate usage to your doctor.
Those with certain eye conditions, including retinitis pigmentosa, may face the risk of vision loss when using Viagra. This medication has been associated with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, which affects eyesight.
Liver or kidney disease can impede the body’s ability to metabolize Viagra, leading to increased side effects. If you suffer from significant impairment in these organs, discuss alternative treatments with your physician.
Individuals with severe dehydration or low blood pressure should also consider avoiding Viagra. These conditions can amplify the risk of adverse reactions. Ensure your overall health status is stable before engaging in this treatment.
If you have a history of stroke or blood clotting disorders, the use of Viagra may elevate your risk for further vascular complications. Prior consultation with a specialist is advisable.
Discussing your complete medical history with your healthcare provider ensures safe and effective use of Viagra, considering these potential contraindications.
Drug Interactions and Their Impact on Viagra Efficacy
Consult a healthcare professional before combining Viagra with other medications. Specific drug interactions can reduce Viagra’s effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. For instance, nitrates, commonly prescribed for angina, can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure when taken with Viagra. Avoid using them together.
Alpha-blockers, utilized for high blood pressure or prostate issues, can similarly cause orthostatic hypotension when paired with Viagra. Monitor your blood pressure closely under these circumstances.
Antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole, and certain antibiotics like erythromycin can elevate Viagra levels in the bloodstream, increasing the likelihood of side effects. If you are prescribed these drugs, inform your doctor about your Viagra use.
HIV protease inhibitors, such as ritonavir, also impact Viagra metabolism. Lower doses of Viagra may be advisable to prevent adverse effects.
Other medications that affect the liver might alter how Viagra works. Always disclose your complete medication list, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to your healthcare provider.
In summary, open communication with a healthcare provider about current medications is crucial to safely using Viagra. Adjustments may be necessary to maintain both safety and effectiveness.
Risk Factors for Adverse Reactions with Viagra
Individuals considering Viagra must assess specific risk factors that could lead to adverse reactions. Monitoring these factors helps enhance safety and effectiveness during treatment.
Cardiovascular Conditions
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and angina, elevate the risk of severe complications. Patients with a history of heart problems should engage with healthcare providers to determine suitability for Viagra.
Drug Interactions
Several medications can interact negatively with Viagra, increasing the likelihood of adverse effects. Always inform healthcare professionals about all medications currently being taken, particularly:
| Medication | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|
| Nitrates | Severe hypotension |
| Alpha-blockers | Low blood pressure |
| Antidepressants | Possible diminished efficacy |
| Antifungals | Increased risk of side effects |
Patients must also avoid mixing Viagra with recreational drugs, such as “poppers,” as these substances can lead to dangerous cardiovascular issues.
Underlying Health Issues
Patients with conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or liver issues may experience heightened risk of side effects. Regular check-ups and a clear health history discussion are essential.
Evaluating these factors in collaboration with healthcare providers optimizes treatment safety and effectiveness for individuals using Viagra.
Consultation and Assessment Before Viagra Prescription
Prior to prescribing Viagra, a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history and current health status is necessary. Initiate the conversation by inquiring about any existing cardiovascular conditions, as these can significantly impact the safety of using this medication. Collect information on any other medications the patient is currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions.
Assessing Risk Factors
Evaluate risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, as they may influence erectile dysfunction and the appropriateness of Viagra. Conduct relevant tests if needed, like blood pressure checks and blood sugar levels, to gauge overall health. Discuss lifestyle choices like smoking and alcohol consumption, which may affect the efficacy of the treatment and the patient’s overall wellbeing.
Patient Education
Educate the patient on how Viagra works, its potential side effects, and the correct usage guidelines. Emphasize the importance of adhering to prescribed dosages and following up if symptoms persist or worsen. An understanding of contraindications, such as those related to nitrates and certain blood pressure medications, plays a critical role in ensuring safe use. Encourage open communication regarding any concerns they may have about the medication.